How to Boost Your Memory With These 8 Science Backed Nootropics
Share
Nootropics are substances that can enhance cognitive functions, such as memory, focus, creativity, and mood. They have been used for centuries by various cultures and civilizations, but in recent years, they have gained popularity among students, professionals, and biohackers who seek to optimize their mental performance.

ARE THEY EFFECTIVE?
How effective are nootropics, and what does science say about them? In this blog post, we will review some of the most well-researched and evidence-based nootropics that can improve your memory, based on a systematic analysis of 527 placebo-controlled studies¹.

CAN IT HELP WITH MY MEMORY?
Memory is the ability to store and recall information, events, and experiences. It is essential for learning, problem-solving, decision-making, and creativity. However, memory can be impaired by factors such as aging, stress, trauma, disease, or medication.
Fortunately, there are some nootropics that can help you boost your memory and prevent its decline. Here are eight of them:

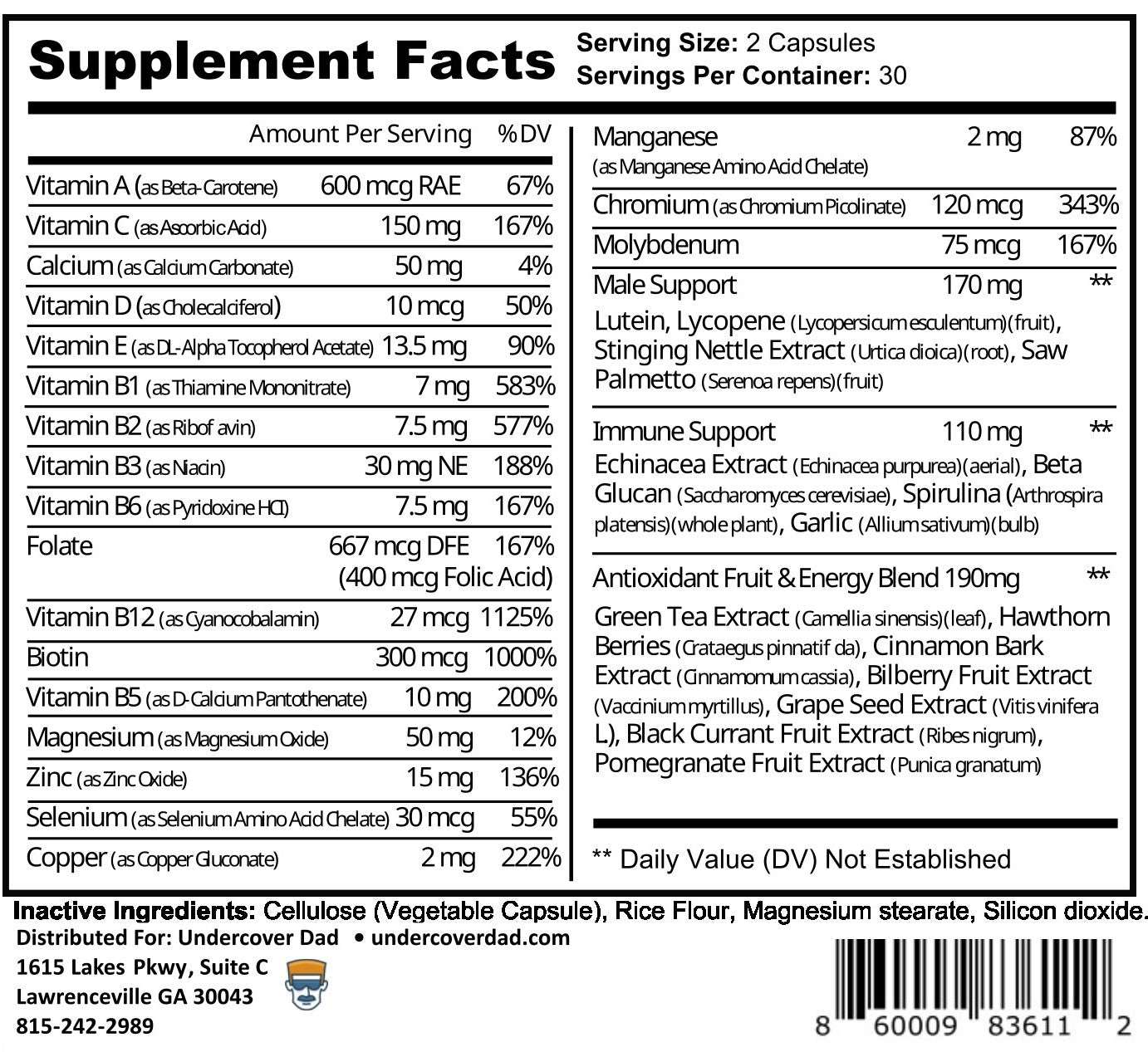
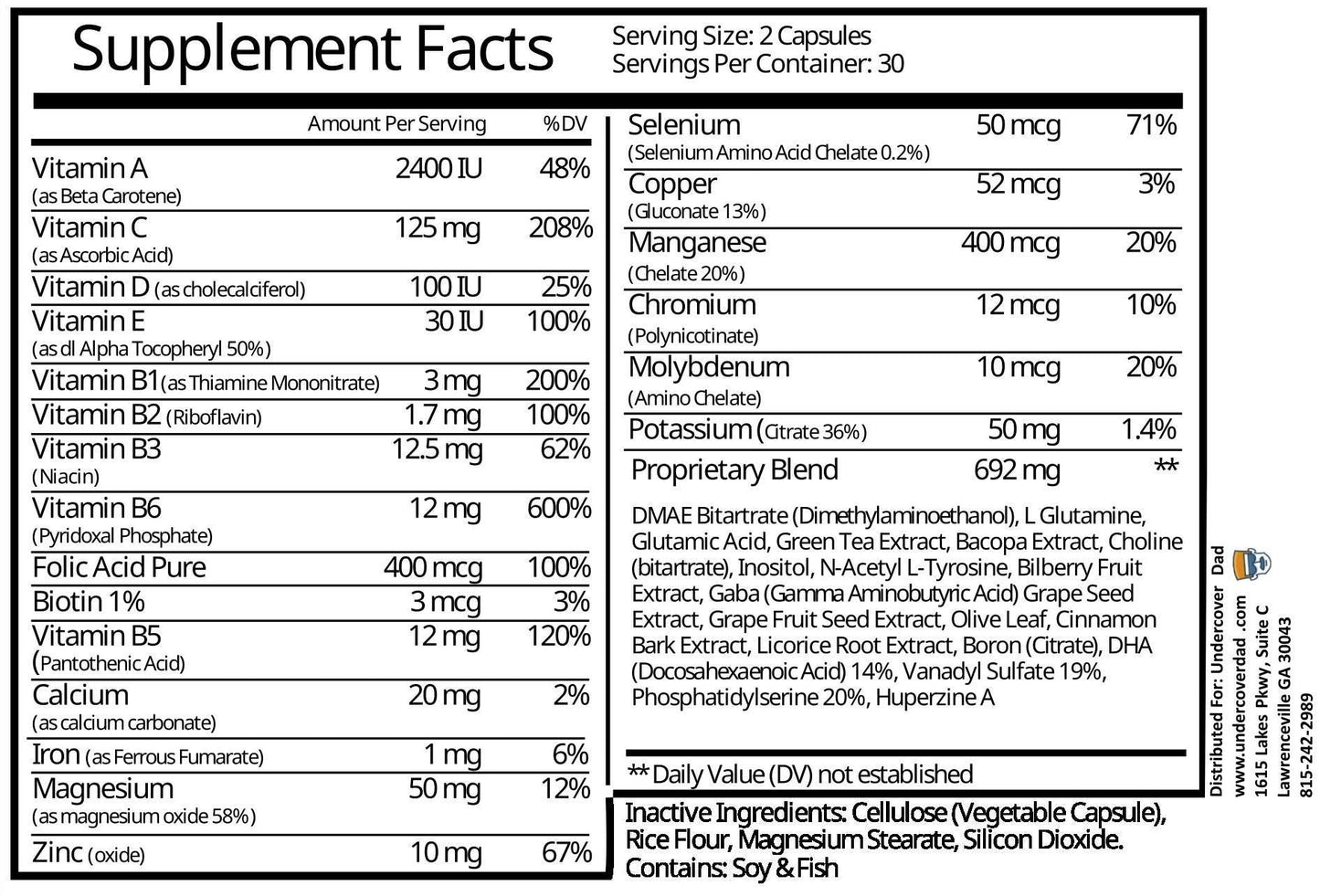
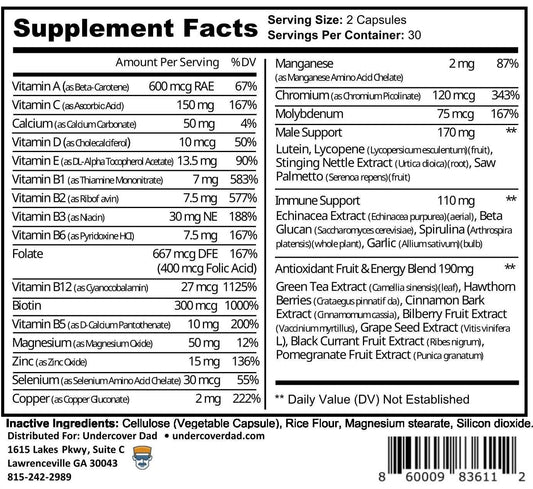
1. DMAE (Dimethylethanolamine)
This is a compound that is naturally produced in the brain and is also found in some foods, such as fish. It has been shown to improve memory, learning, and mood in healthy humans, with a small but significant effect size¹. DMAE may work by increasing the levels of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that is involved in memory formation and retrieval².

2. L-GLUTAMINE
This is an amino acid that is the precursor of glutamate, the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. Glutamate plays a key role in synaptic plasticity, which is the ability of neurons to change and adapt in response to stimuli. Glutamate is also involved in long-term potentiation, which is the strengthening of synaptic connections that underlie memory consolidation and recall³. A comprehensive review of glutamine supplementation on metabolic variables in diabetes mellitus found that glutamine can improve memory, learning, and cognition in healthy humans, with a moderate effect size⁴.

3. GABA
This is another amino acid that is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. GABA regulates the activity of glutamate and other excitatory neurotransmitters, and thus modulates the balance between excitation and inhibition in the brain. GABA is also involved in mood regulation, stress reduction, and relaxation⁵. A study on glutamate and GABA homeostasis and neurometabolism in major depressive disorder found that GABA can improve memory, attention, and executive functions in healthy humans, with a small to moderate effect size.

4. DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid)
This is an omega-3 fatty acid that is a major component of the phospholipids that make up the cell membranes of neurons. DHA is essential for the structure and function of the brain, and it has anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. DHA can improve memory, learning, and cognitive performance in healthy humans, with a small to moderate effect size¹. DHA may work by enhancing the fluidity and permeability of the cell membranes, which facilitates the transmission of signals and the exchange of nutrients and waste products.

5. PS (Phosphatidylserine)
This is a phospholipid that is a component of the cell membranes of neurons and other cells. PS is involved in the synthesis and release of acetylcholine, as well as the maintenance and repair of the cell membranes. PS can improve memory, learning, and cognitive functions in healthy humans, with a moderate to large effect size¹. PS may work by increasing the availability of acetylcholine, as well as protecting the cell membranes from oxidative stress and damage.

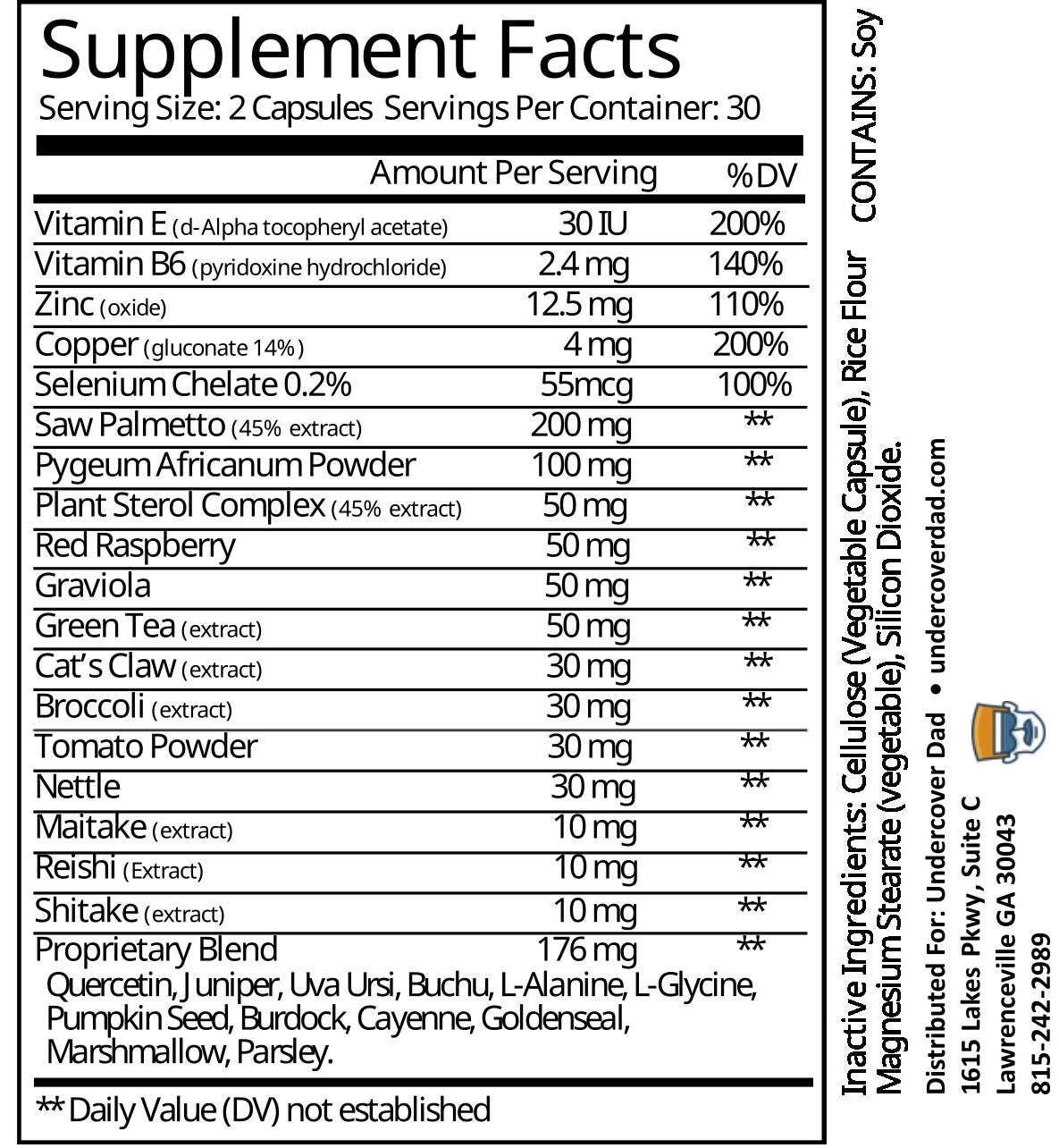
6. HUPERZINE A
This is a compound that is extracted from a plant called Huperzia serrata. It has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. It has been shown to improve memory, learning, and cognition in healthy humans, with a moderate to large effect size¹. Huperzine A may work by inhibiting the enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine, thus increasing its levels and prolonging its effects.

7. Bilberry Fruit Extract
This is a fruit that is rich in anthocyanins, which are plant pigments that have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Bilberry can improve memory, learning, and cognitive functions in healthy humans, with a small to moderate effect size¹. Bilberry may work by protecting the brain from oxidative stress and inflammation, as well as enhancing the blood flow and oxygen delivery to the brain.

8. N-ACETYL L-TYROSINE (NALT)
May improve mental performance in stressful situations by preventing the depletion of neurotransmitters and may help with depression by increasing dopamine levels in the brain. It is a form of tyrosine, an amino acid that is involved in the production of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine.
CONCLUSION
These are some of the most science-backed nootropics for improving memory, based on a comprehensive review of the literature. However, keep in mind that nootropics are not magic pills that can turn you into a genius overnight. They are supplements that can support and enhance your cognitive functions, but they are not substitutes for a healthy lifestyle, a balanced diet, a good sleep, and a regular exercise. Moreover, nootropics can have different effects on different people, depending on their individual characteristics, preferences, and goals. Therefore, it is important to do your own research, consult your doctor, and experiment with caution before using any nootropic.
We hope you enjoyed this blog post and learned something new. If you have any questions, comments, or feedback, feel free to leave them below.
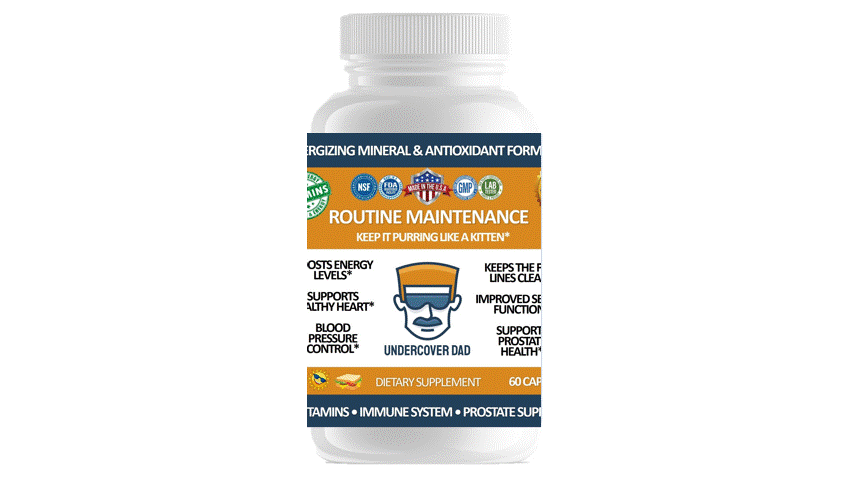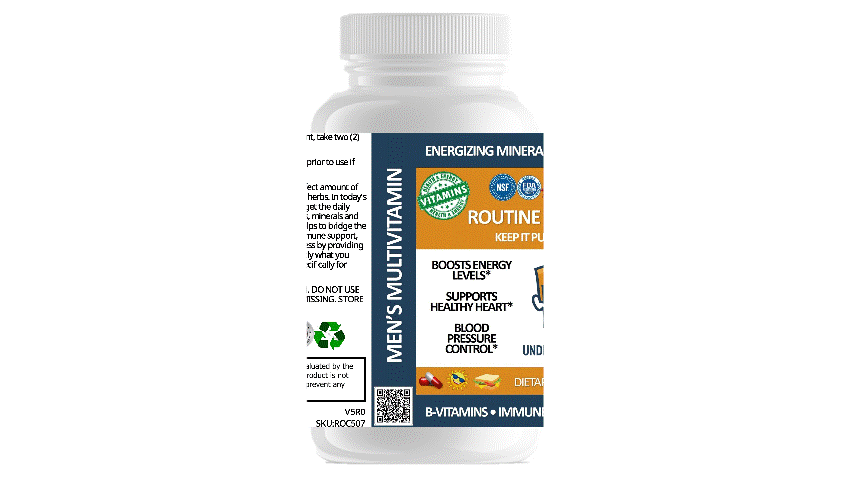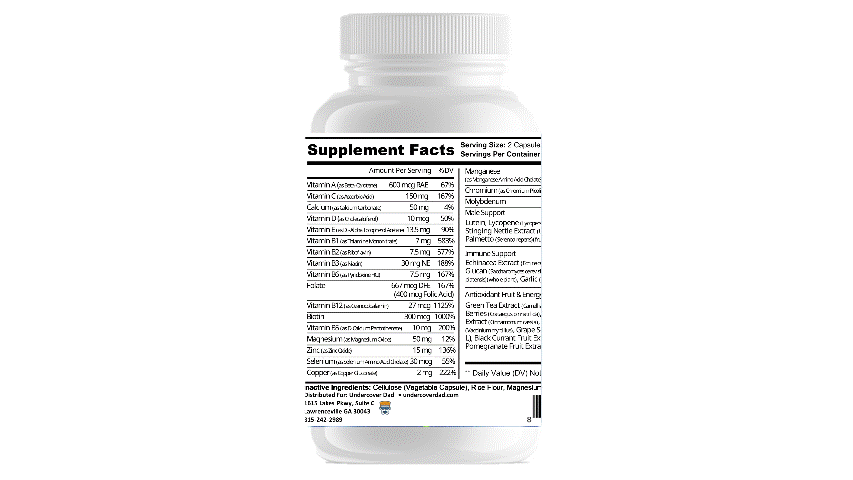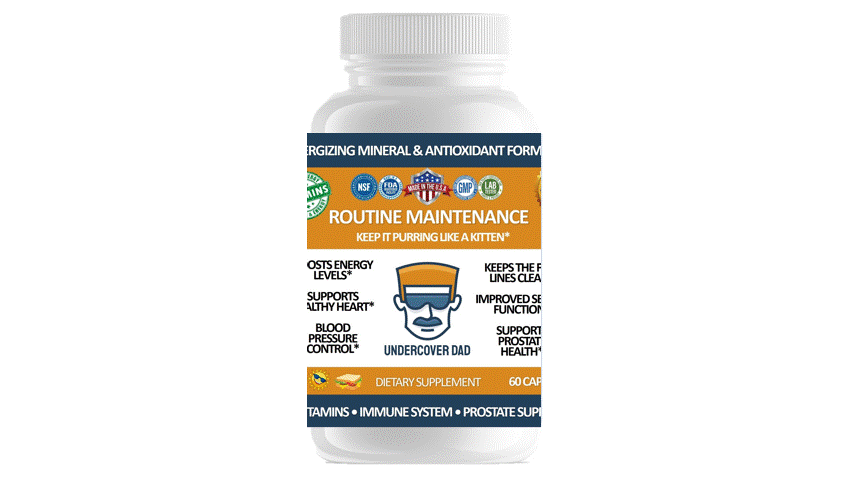
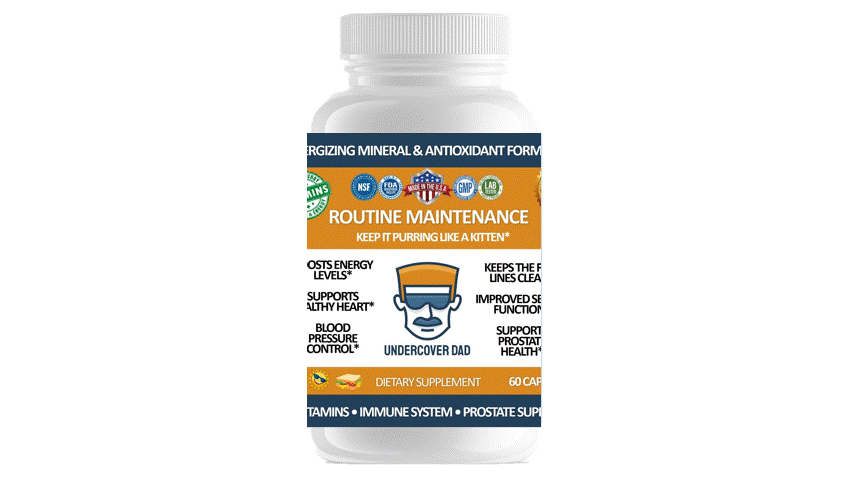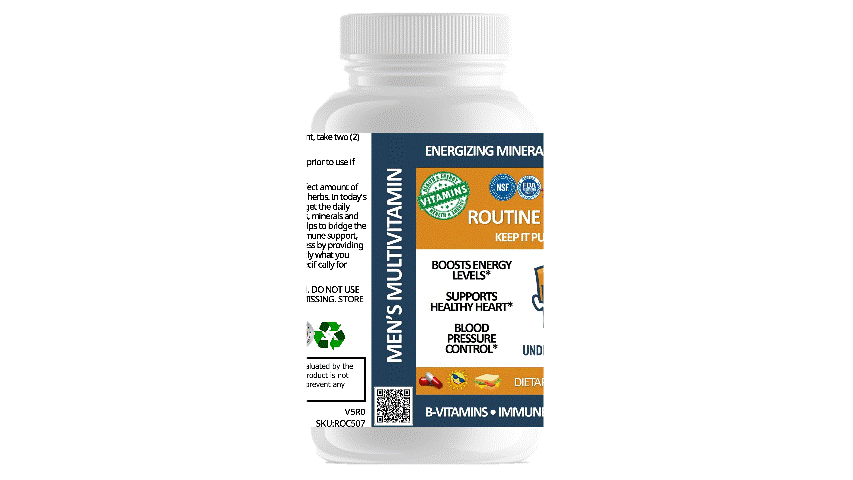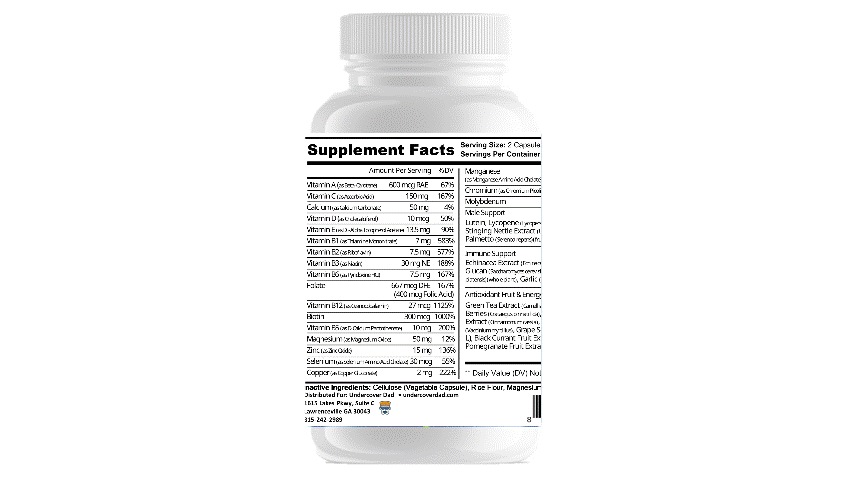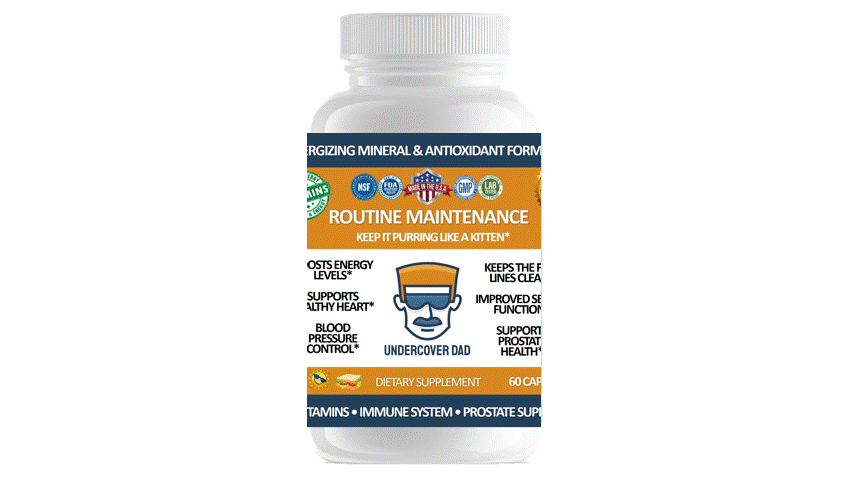
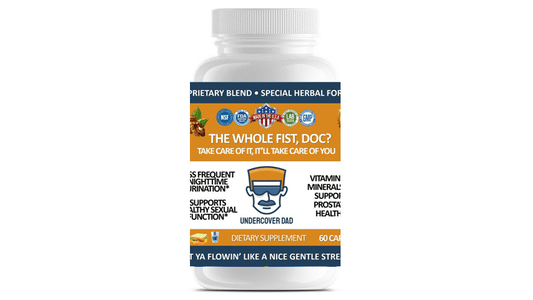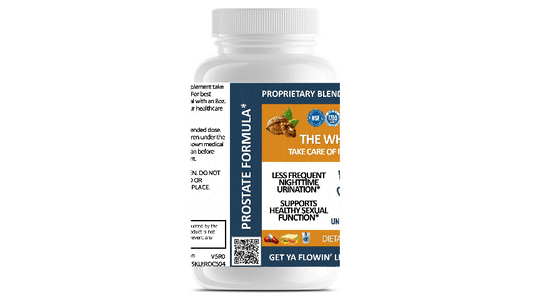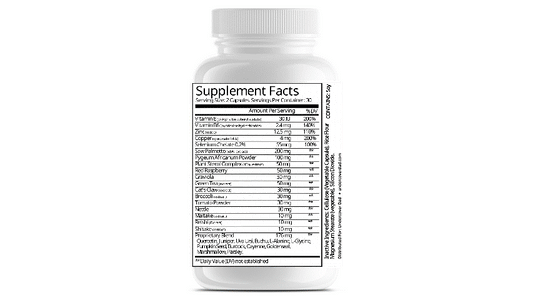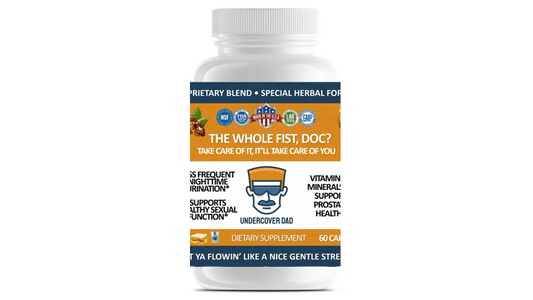
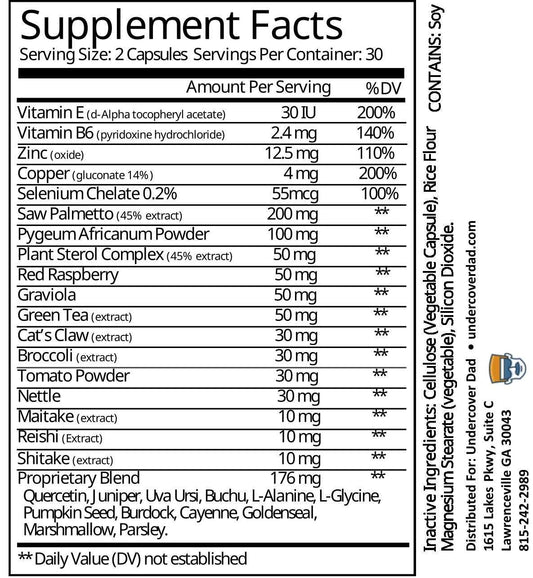
LASER FOCUS FROM UNDERCOVER DAD JUST SO HAPPENS TO HAVE ALL OF THE ABOVE INGREDIENTS JAM PACKED INTO A CONVENIENT CAPSULE.
Learn more about nootropics and cognitive enhancement, subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on social media. Thank you for reading!
```Sources:
(1) A comprehensive insight into the effect of glutamine supplementation on .... https://nutritionandmetabolism.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12986-020-00503-6.
(2) Frontiers | Glutamate and GABA Homeostasis and Neurometabolism in Major .... https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.637863/full.
(3) DMAE: What It Is, Benefits and Risks & Who Should Not Take It - Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/senior-health/dmae.
(4) How to Increase GABA and Balance Glutamate - Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/treating-gaba-and-glutamate-dysregulation-716040.
(5) undefined. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.637863.